Positive effects of plants
Why are plants so important to us?
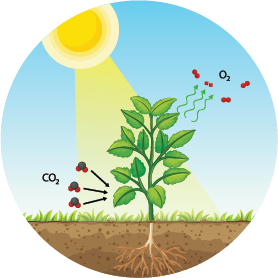
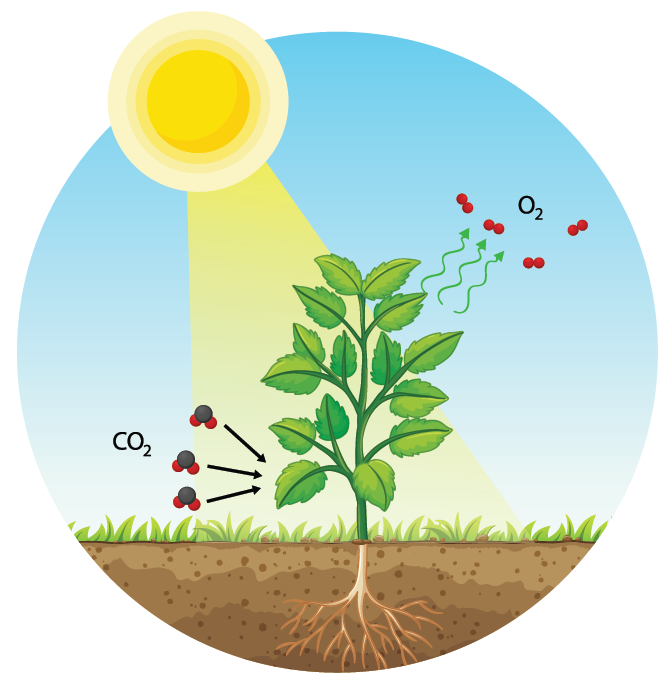
Plants have many positive qualities. Through photosynthesis, plants produce the oxygen that is vital for humans and animals, and which purifies the air as well. For many animals, plants form a space to live – from small animals living in moss to large animals living in the forest. Through evaporation, plants have an influence on the microclimate. A larger arrangement of plants such as hedges or forests can even serve as noise protection. In the case of green façades and roofs, they even function as thermal insulation. And let us not forget, of course, the nutrition aspect and aesthetic effect that plants have on the environment and on our well-being.
BENEFITS FOR GREEN COOL SCHOOLS

- Motivating the pupils to make the school “greener” together, value plants and care for them, including taking the message home with them.
- Creating a positive attitude amongst pupils and school staff towards plants. Increasing awareness of the positive effects of plants and their importance.
- Collecting arguments for greening your school, which helps you to raise money and receive support from administration, politics as well as parents.
Improving air quality and reducing noise
Plants have the ability to filter pollutants through their leaf surface and thus make a significant contribution to air purification and to binding urban particulate matter. In addition, CO2 is also bound in plants. Through photosynthesis, plants produce the oxygen that is vital for humans and animals, and which purifies the air. Furthermore, the substrates and plants have a noise-absorbing effect, whereby – depending on the arrangement and the degree of coverage of the vegetation, the substrate depth and the materials used – a significant noise reduction can be achieved.
DID YOU KNOW?

When did the first forests develop?
In the Devonian Period (about 370 million years ago) there were already the first forests of tree-like plants. Later, in the Carboniferous Period (320 million years ago), huge swamp forests spread, which lowered the CO2 content of the atmosphere enormously and enriched the oxygen content in the atmosphere to 30 percent.
In Austria, 48 percent of the land area is covered with forest, which corresponds to about four million hectares. The forest areas in Austria are growing because more trees are planted than harvested.
How much oxygen can an average deciduous tree produce in a year?
With an annual rainfall of about 800 millimetres, an average deciduous tree of 15 to 20 metres height can produce about 370 litres of oxygen per hour. Extrapolated to a year, that is about three million litres of oxygen. In comparison, the oxygen consumption of humans per hour, depending on the activity, ranges from 15 litres (at rest) to 150 litres and more (heavy work, sports).

Plants as natural air conditioning
Through evaporation and shading, plants have an influence on the microclimate.
- Plants provide pleasant and natural shade that is perfectly adapted to seasons. In summer, when it is hot, plants provide maximum shade through their leaves. In winter, on the other hand, when we need more light, sun and warmth, the leaves usually fall off.
- Plants also cool their immediate surroundings through evapotranspiration. In this way, green areas in urban spaces act like natural air conditioning. In the case of green buildings, this also leads to a noticeably reduced warming effect on the façades and roofs. They thus not only influence their surroundings, but also ensure more pleasant temperatures inside the buildings.
DID YOU KNOW?

What is evapotranspiration?
Evapotranspiration is the combination of transpiration and evaporation.
- Transpiration is the evaporation of water by the plants through their stomata. They extract heat from the environment, which creates a cooling effect. This effect is comparable to human sweating – human bodies begin to sweat to cool themselves down.
- In addition, there is the evaporation of water from natural soil and water surfaces. Soil and substrates store water and then evaporate it again. This evaporation provides increased humidity, which contributes to greater well-being and cooling.
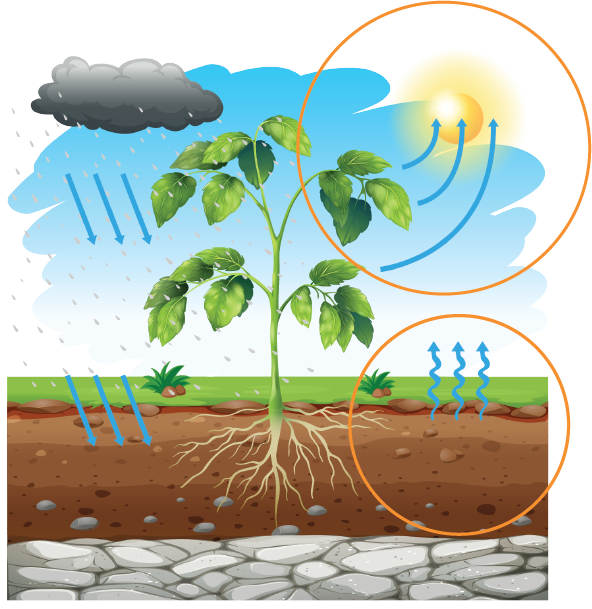
Contribution of plants to rainwater management
Greened areas can retain and store water in that the substrate and the plants absorb the rainwater directly and only evaporate it after a time delay when it is released back into the atmosphere in smaller quantities (water retention). This creates a natural cycle. Between 70 and 80 percent of precipitation can be retained in this way and thus does not end up in the urban sewage system. Sealed surfaces such as concrete and asphalt prevent the infiltration of rainwater. This can subsequently lead to overloading of the municipal sewer system and flooding during heavy rainfall events or when the snow melts in spring.
TIP

Working with the class, make a plan for a schoolyard or car park that does not become a heat trap in summer. What would it look like? Have the pupils draw up a plan on the board or in groups on posters and discuss it together.
Influence on cognitive performance
In addition to these ecological aspects that speak for the use of green plants on school grounds, plants can also contribute significantly to improving the ability to concentrate. Nancy M. Wells, for example, found a significant improvement in cognitive functions in a study of children who had moved from urban areas to greener surroundings. The greater the changes from the previous (vegetation-free) home to the new (greener) home, the better the children’s ability to focus their attention.
OPPORTUNITIES TO DEEPEN THE TOPIC ACROSS DISCIPLINES

As an interdisciplinary consolidation you can work on the following questions with the pupils:
- What happens during photosynthesis?
- Pupils explain the process of photosynthesis and discuss its role for the environment and humans.
- What characteristics should a schoolyard have?
Discuss the characteristics of an ideal schoolyard that meets the needs of the pupils.
- What role do plants play in the city?
- Consider different plant locations in the city.
- Give examples of plants that grow in the city.
- Discuss the importance of plants for life in cities.
- What types of surfacing materials and soil sealing allow water to pass through?
- Describe the role of plants and soil in the water cycle and derive contributions for sustainable rainwater management. Name different soil coverings and their technical terms.
Experiments
Experiment: Measuring water storage capacity
Measuring water storage capacity The experimental set-up is used to simulate a rainfall event on vegetated, open, and sealed ground. In this way, soil erosion and the effect of plants are illustrated. In addition, the different effects of rain on…


